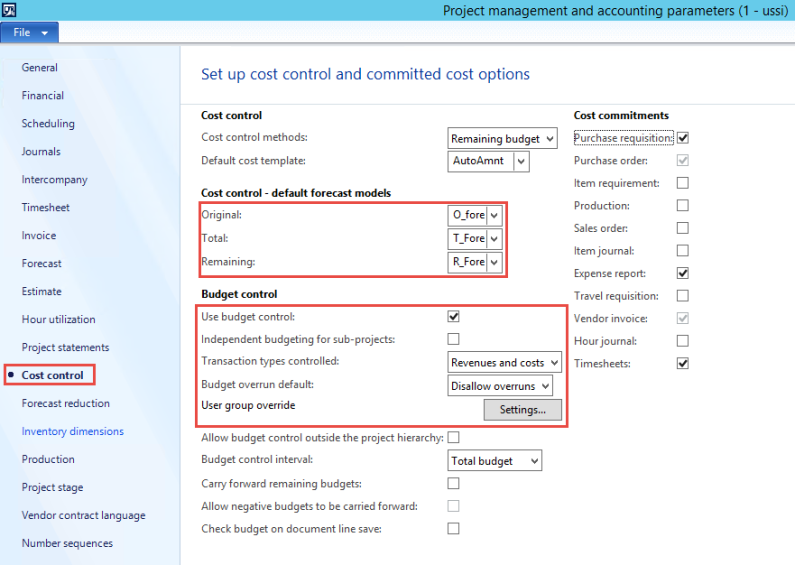
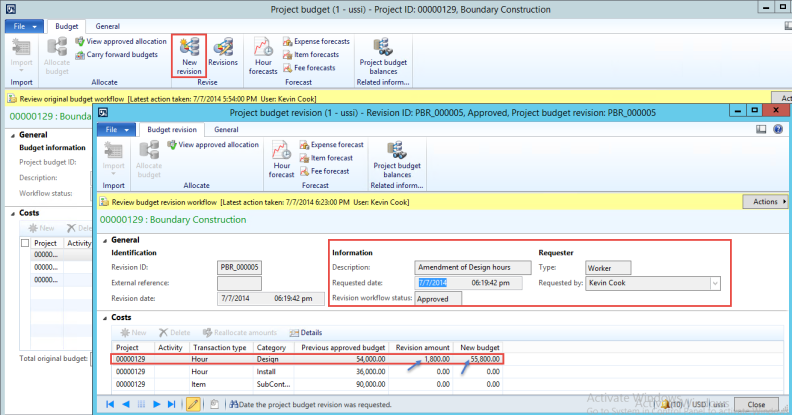
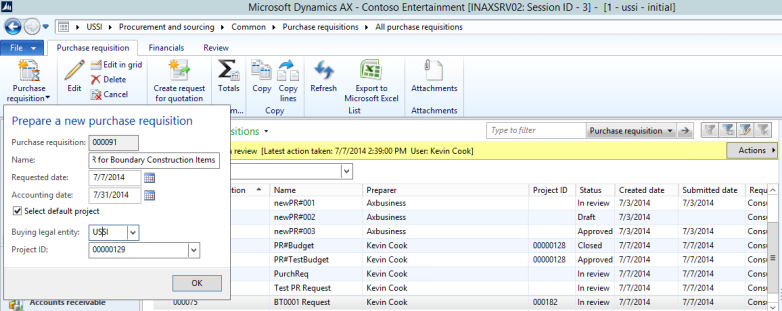
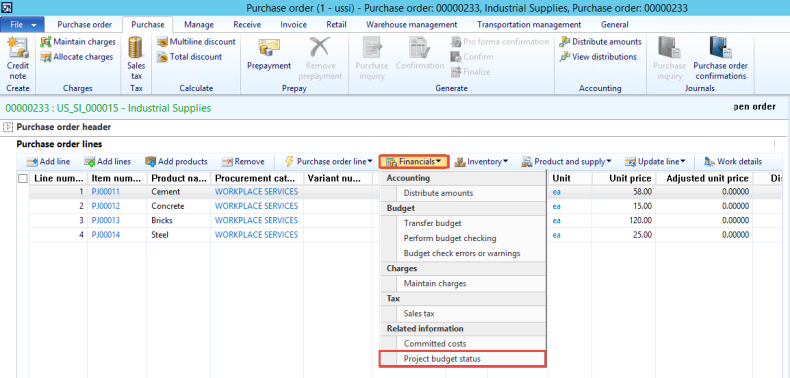
Native Support for Parallel Accounting for transition to IFRS
Microsoft Dynamics AX have posting layers in the General Ledger and for consolidation that allow it to be one of the unique ERPs that allow for parallel accounting that is needed as part of a transition to IFRS. Microsoft Dynamics AX has 3 layers – one primary and two adjustment layers. The layers are Current, Operations and Tax. For example, the diagram below represents a USA public company listed in the United States that has a public holding company in Europe and needs to report in 3 formats: Tax for the IRS, US GAAP for the SEC and public filings in the United States and IFRS as adopted by the EU for group external reporting. Layer 1 is the ‘Current’ Layer in Microsoft Dynamics AX holds the US GAAP postings. Layer 2 is the Operations Layer and has any IFRS Delta postings. Fixed Asset can be posted in full for all layers so those do not require any deltas as they can automatically post into multiple layers by setting up a dependency through Value models. Effectively this allows the Fixed Asset Sub Ledger to have a full US GAAP, IFRS and Tax set of books in it. Any Tax adjustments or other Tax posting are made in the Tax Layer e.g. Section 179 accelerated depreciation for qualifying assets.

Figure: Microsoft Dynamics AX provides support for multiple posting layers such as current, operations and tax that provide it with unique capability to have native support for parallel accounting. Source of this screen shot is Microsoft Corporation.
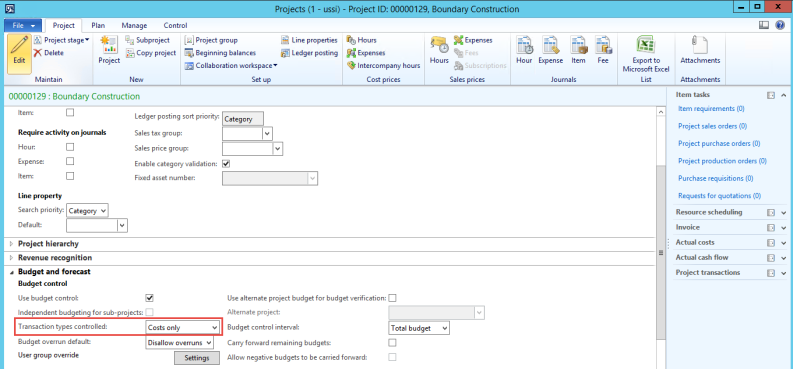
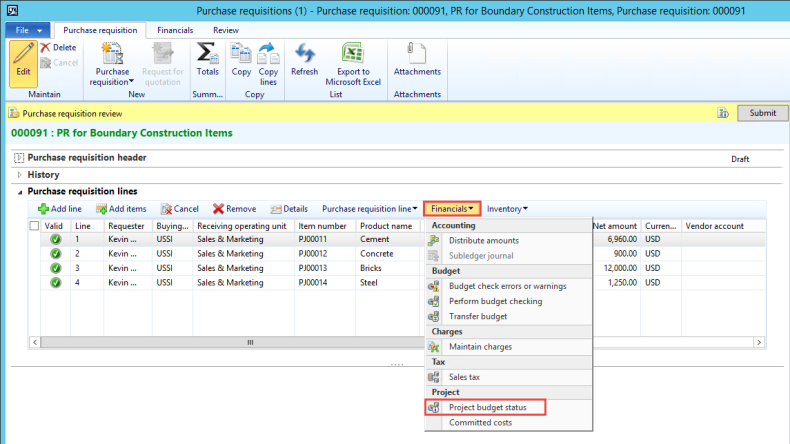
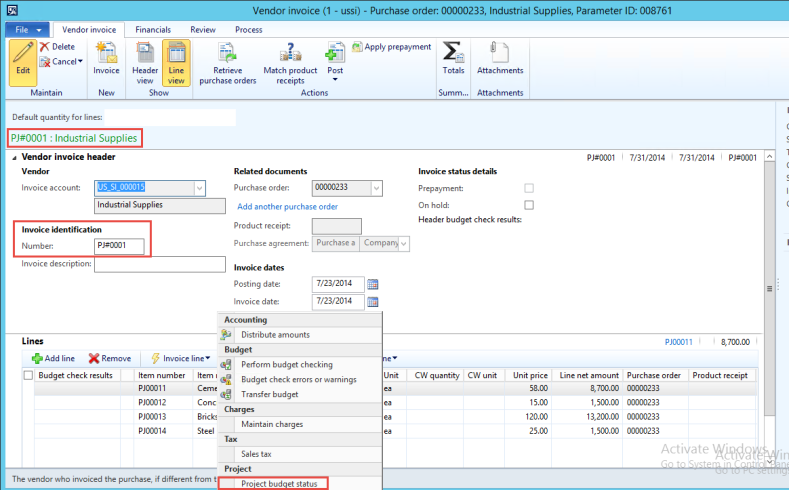
Microsoft Dynamics AX has the ability to have different journals post to different layers. For example, I can have a regular GL Journal that posts to the Current (US GAAP layer in our example) and an IFRS General Ledger Journal that posts to the Operations (IFRS Layer in our example)

Figure: Microsoft Dynamics AX support the transition to IFRS with ability to support parallel accounting with different posting layers. In this screenshot, the IFRS GL Journal is posting to the Operations Layer for any IFRS Delta postings
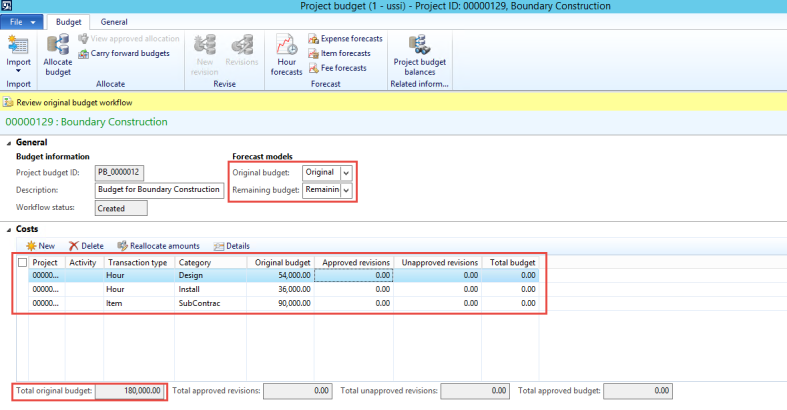
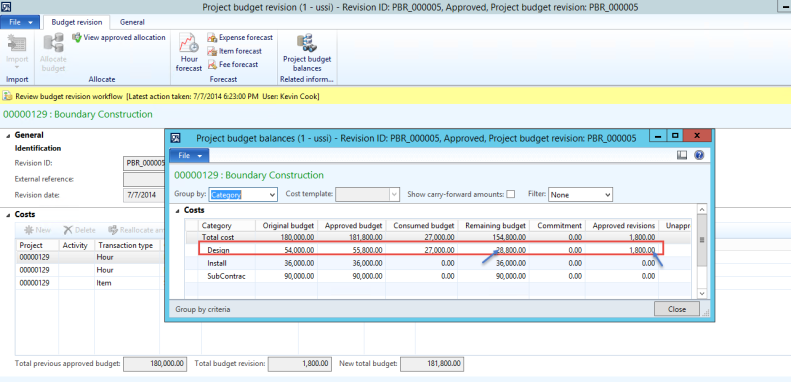
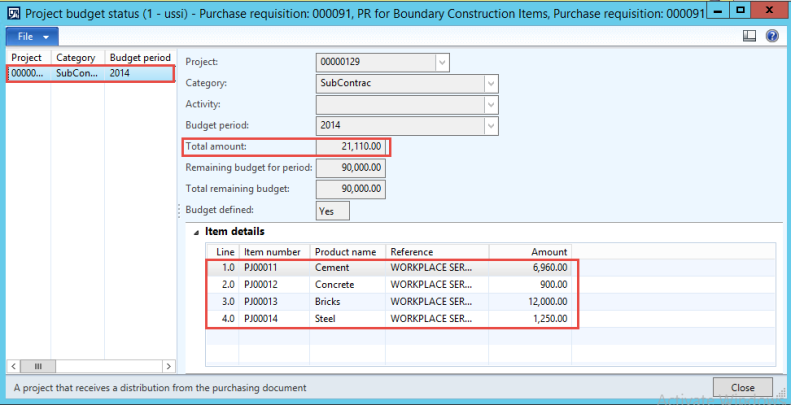
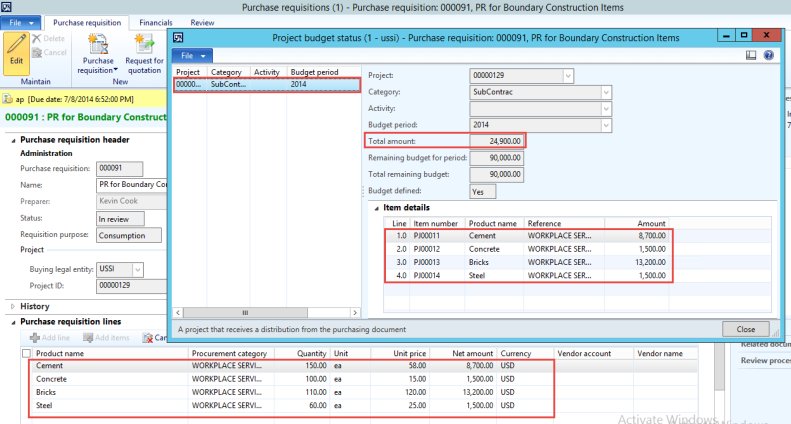
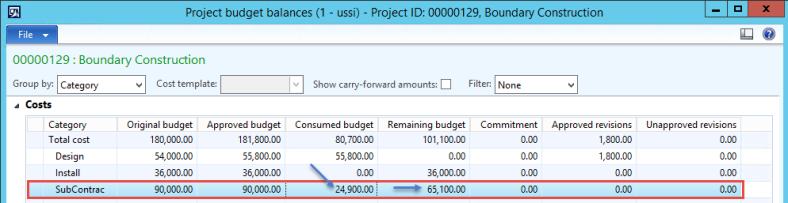
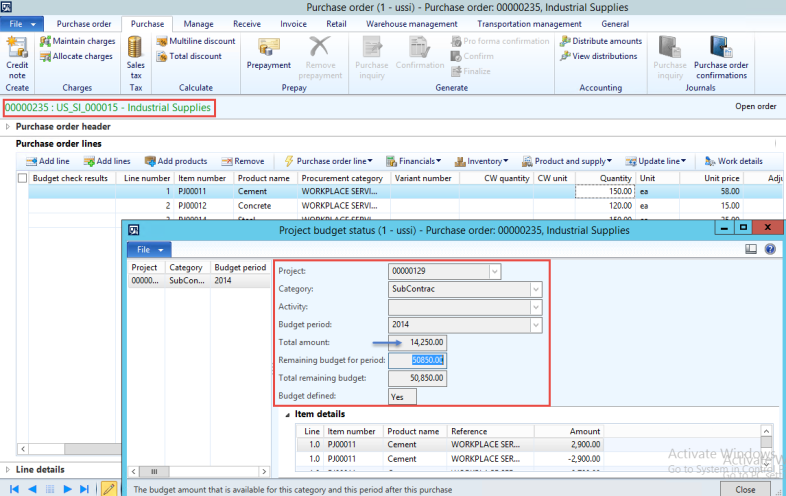
The reporting structure in Microsoft Dynamics AX then allows you to define on the report where you would like the numbers to come from. We can setup a report for US GAAP by choosing the layer as Current and then we can use the same report or a copy of it by setting the source posting layer as Operations plus current and it would show us the IFRS numbers.

Figure: Cash Flow report in Microsoft Dynamics AX showing that the posting layer can be selected on the report definition allowing the same report definition to be used to get numbers in different accounting standards such as US GAAP, IFRS and Tax thus simplifying accounting and reporting greatly.
First Time adoption of IFRS (IAS 1)
IAS 1 requires that businesses adopting IFRS maintain a comparative year and also requires that an ERP system should be able to load or post manual adjustments for the IFRS opening balance in either the last period before the transition date and then roll-forward the IFRS opening balance or in the period of the transition date with a specific identifier in order to track and distinguish the opening balance adjustments for IFRS from regular transactions.
From a Financial system stand-point this requires the following
- Recording of opening balances
- Multiple year over year reporting required
- Adjusting of opening balances under IFRS
- Ability to separately identify normal accounting transactions from those for IFRS adjustments
In Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012, the opening transactions can be posted to a unique period (the opening period) of the fiscal year through import of transactions of by transferring prior year ending balances. Prior year ending balances are transferred to the opening period. The opening period is a special period compared with the normal transaction periods. The opening period is usually the first period of a new fiscal year (for example,it covers only the first day).
Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 alsohas a closing periodwhere the closing transactions can be posted. A closing sheet can be created to create closing transactions. When creating the closing sheet, manual adjustments can be created and posted. Multiple closing sheets can be created for different purposes, and each can be uniquely identified. E.g. you can have a regular closing sheet and then another one to record the IFRS transition adjustments. For example, the screen shot below shows that the GAAP Closing sheet is posted in the current layer while the IFRS Closing sheet with relevant adjustments is posting to the Operations Layer.

Figure: The Closing Sheet in Microsoft Dynamics AX can post to different layers to record adjusting transactions for the IFRS and be able to identify them separately
In addition IAS1 specifies the need for two statements of comprehensive income, two separate income statements, two statements of cash flows, two statements of changes in equity, related notes, including comparative information. All of this is achieved by having the different layers and running reports either via Management Reporter or the Dynamics AX Financial Statements and selecting the appropriate layer or combination of layers as illustrated in the Cash flow example above.
XBRL Support:
The IFRS has adopted the XBRL Taxonomy as its standard for electronic exchange of financial data prepared in accordance with the IFRSs. TheIFRS Foundation XBRL Team is responsible for developing and maintaining the XBRL representation of the IFRSs, known as the IFRS Taxonomy. Both IFRSs and XBRL are intended to standardize financial reporting in order to promote transparency and to improve the quality and comparability of business information, therefore the two form a perfect partnership. As shown in the screen shot below, Microsoft Dynamics AX has native support for XBRL with the ability to natively to import an XBRL taxonomy and use it very quickly. The IFRS in March 2011 published 12 sample XBRL samples including Statements of Financial Position,Comprehensive Income, andChanges in Equity, Statement of Cash Flows, Employee benefits obligations, Consolidated and separate Statements of Financial Position. Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 can very quickly allow you to take these examples and start reporting in XBRL.

Figure: Microsoft Dynamics AX provides native support for XBRL
In addition Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 provides support for drag and drop type editors for the presentation of reports, calculations, labels etc. that make XBRL a fairly straight forward process.

Figure: XBRL Taxonomy details for the Presentation of Financial Statements in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012

Figure: Formulas in XBRL Taxonomy for Calculation for Financial Statements in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012
The imported XBRL Taxonomy works with the Microsoft Dynamics AX Reports Structure Designer and the Management Reporter Tool that can be used to generated reports. The screen shot below shows the native structure designer with the XBRL Income Statement.


Figure: Microsoft Dynamics AX Report Row Structure Designer showing the XBRL Taxonomy that was imported from the xbrl.org. The first screen shot shows the row definition and the second one show the simulation with the row labels (notice the simulate check box is checked which forces it to simulate the structure of a published report)